Monday, January 4, 2010
Dabigatran etexilate a better drug than warfarin for VTE?.
Thursday, July 21, 2016
New oral blood thinners can decrease stroke risk in atrial fibrillation patients without frequent monitoring
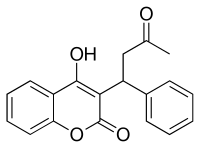
 Dabigatran
Dabigatran  Rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939)
Rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939)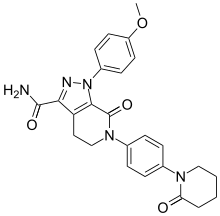 Apixaban
Apixaban  Edoxaban
EdoxabanWednesday, January 11, 2012
Dabigatran, New Blood Thinner Linked To Higher Heart Attack Risk
Sunday, November 7, 2010
FDA approves Pradaxa to prevent stroke in people with atrial fibrillation....
Pradaxa is an anticoagulant that acts by inhibiting thrombin, an enzyme in the blood that is involved in blood clotting. The safety and efficacy of Pradaxa were studied in a clinical trial comparing Pradaxa with the anticoagulant warfarin. In the trial, patients taking Pradaxa had fewer strokes than those who took warfarin.
"Unlike warfarin, which requires patients to undergo periodic monitoring with blood tests, such monitoring is not necessary for Pradaxa," Dr. Norman Stockbridge(director of the Division of Cardiovascular and Renal Products in the FDA's ) says.
Pradaxa, manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. of Ridgefield, Conn., will be available in 75 milligram and 150 milligram capsules....
Ref : http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm230241.htm
Thursday, April 12, 2018
Aspirin as Good a Clot Buster as Pricey Drugs After Joint Replacement
"From this study, we have no evidence to support starting aspirin on day one," Anderson said.
"This study reinforces that," Bozic said.
"The strategy for preventing clots should include medication and early mobilization," he stressed.

