Sense oligonucleotide antidote reverses actions of antisense antithrombotic drug, prevents bleeding
Tuesday, November 24, 2015
Sense oligonucleotide antidote reverses actions of antisense antithrombotic drug, prevents bleeding
Sense oligonucleotide antidote reverses actions of antisense antithrombotic drug, prevents bleeding
Saturday, May 24, 2014
Compound reverses symptoms of Alzheimer's disease in mice
Farr cautioned that the experiment was conducted in a mouse model. Like any drug, before an antisense compound could be tested in human clinical trials, toxicity tests need to be completed.
Antisense is a strand of molecules that bind to messenger RNA, launching a cascade of cellular events that turns off a certain gene.
In this case, OL-1 blocks the translation of RNA, which triggers a process that keeps excess amyloid beta protein from being produced. The specific antisense significantly decreased the over expression of a substance called amyloid beta protein precursor, which normalized the amount of amyloid beta protein in the body. Excess amyloid beta protein is believed to be partially responsible for the formation of plaque in
the brain of patients who have Alzheimer's disease.
Scientists tested OL-1 in a type of mouse that overexpresses a mutant form of the human amyloid beta precursor gene. Previously they had tested the substance in a mouse model that has a natural mutation causing it to overproduce mouse amyloid beta. Like people who have Alzheimer's disease, both types of mice have age-related impairments in learning and memory, elevated levels of amyloid beta protein that stay in the brain and increased inflammation and oxidative damage to the hippocampus the part of the brain responsible for learning and memory.
"To be effective in humans, OL-1 would need to be effective at suppressing production of human amyloid beta protein," Farr said.
Scientists compared the mice that were genetically engineered to overproduce human amyloid beta protein with a wild strain, which served as the control. All of the wild strain received random antisense, while about half of the genetically engineered mice received random antisense and half received OL-1.
The mice were given a series of tests designed to measure memory, learning and appropriate behavior, such as going through a maze, exploring an unfamiliar location and recognizing an object.
Scientists found that learning and memory improved in the genetically engineered mice that received OL-1 compared to the genetically engineered mice that received random antisense. Learning and memory were the same among genetically engineered mice that received OL-1 and wild mice that received random antisense.
They also tested the effect of administering the drug through the central nervous system, so it crossed the blood brain barrier to enter the brain directly, and of giving it through a vein in the tail, so it circulated through the bloodstream in the body. They found where the drug was injected had little effect on learning and memory.
Ref http://iospress.metapress.com/content/px72758w0158103u/?issue=4&genre=article&spage=1005&issn=1387-2877&volume=40
Saturday, July 28, 2012
Antisense Pharma presents data from trabedersen Phase I/II cancer study at ASCO 2012
Wednesday, May 18, 2016
New drug shows promise against Huntington's disease
Sunday, June 21, 2009
Antisense drug in combination with paclitaxel for prostate cancer..
 I think when I was doing some reference work for my research in 1996, I read about this drug (taxol) [In 1994 the total synthesis has been achieved by Robert Holton of Florida University. He did spend 12 years to achieve the total synthesis because of the assymmtery involved in it [It was after 40 years' after the first exctract from the tree Pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia) has shown anticancer activity and the key ingrediant identified was taxiol]. A diterpenoid, with androgen (a male hormone) blockade chemotherapy has played important role in the treatment of cancer.
I think when I was doing some reference work for my research in 1996, I read about this drug (taxol) [In 1994 the total synthesis has been achieved by Robert Holton of Florida University. He did spend 12 years to achieve the total synthesis because of the assymmtery involved in it [It was after 40 years' after the first exctract from the tree Pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia) has shown anticancer activity and the key ingrediant identified was taxiol]. A diterpenoid, with androgen (a male hormone) blockade chemotherapy has played important role in the treatment of cancer.Prostate cancer is the second most frequently diagnosed cancer in men after skin cancer. It is estimated there will be 218,890 new cases diagnosed in the U.S. this year(2009). Around 1 in 6 men will develop prostate cancer, a third to a half of whom will recur after local treatment and risk progression to metastatic prostate cancer. Metastatic disease invariably progresses to hormone refractory or castrate resistantprostate cancer (CRPC) if given enough time.
More interesting and significant results have been achieved by an Australian company (Antisense Therapeutics). i.e., in combination with taxol, antisense drug ATL1101 has yielded good results. ATL1101 is a second generation antisense inhibitor of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) which as reported previously suppressed the growth of human prostate tumors in an animal model of prostate cancer, and slowed down transition to CRPC when used as a single agent.
The research is of great importance because of the fact that in cell culture experiments, the amount of Paclitaxel required to induce tumor cell apoptosis (cell death) was significantly reduced when used in combination with ATL1101. This ability to 'sensitize' tumor cells to the cytotoxic effects of Paclitaxel affirms ATL1101's potential as a chemo-sensitizing agent to be used in combination with existing prostate treatments to improve the outcomes for patients.
I did work for some of the intermediates (ologonucleotides) for ISIS (contract research) and am excited to see that this company has tie up with ISIS. In my opinion as ISIS , is an established company in this field of research, hope soon there will be relief for those patients for whom CRPC, treatment options are limited and prognosis is poor....
Ref: http://www.antisense.com.au/!upload_files%5Cattachment%5Casx%2009%2018%20June%202009_ATL1101.pdf
Tuesday, September 11, 2018
New approach to kill specific bacteria could be alternative to antibiotics
"We were able to show that these drugs can zero in on and kill C. difficile bacteria while leaving other bacteria alone," said Arun Sharma, associate professor of pharmacology, Penn State College of Medicine. "We're still working to refine these drugs and make them even better, with the eventual goal of testing them clinically."
"These drugs are organism specific, meaning that they target only one kind of bacteria, kind of like smart antibiotics," Stewart said. "They're precise. And that's especially important with C. difficile infections because this bacteria is uniquely, selectively advantaged to exploit ecological disturbances in the human gut."
"Ideally, a treatment for C. difficile would have no effect on other bacteria," Stewart said.
"Our antisense antibiotics contain genetic material which is complementary to bacterial genetic material, so we designed our genetic material to target specific genes in C. difficile," Stewart said. "And when our genetic material binds to the bacterial genetic material, it prevents the expression of bacterial genes. And that can cause C. difficile to die."
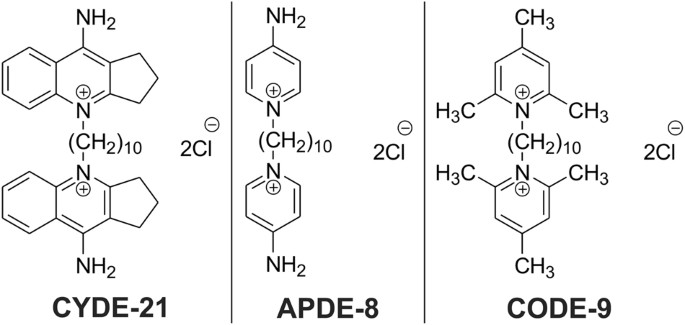
"Ultimately, we wanted these compounds to deliver the drug into the C. difficile bacteria without hurting other bacteria or the patient," Sharma said. "After testing these three, we found that one carrier in particular -- CYDE-21 -- was the best at delivering an effective dose of the drug into the bacteria."
Saturday, May 19, 2012
Isis Initiates Phase 1 Study in Patients With Cancer With the First Generation 2.5 Antisense Drug, ISIS-STAT3Rx
Isis Initiates Phase 1 Study in Patients With Cancer With the First Generation 2.5 Antisense Drug, ISIS-STAT3Rx
Ref : http://ir.isispharm.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=222170&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1691711&highlight=
Saturday, October 24, 2009
Phase III clinical study of trabedersen....
Ref :http://www.anticancer.de/index.php?id=38.
I found this video, interesting (mode of action of trabedersen)
Sunday, May 10, 2009
RNA interference approach for prevention and treatment of STDs ?
In my earlier blog “Diverse use of Nucleic acids”, did mention that there is much interest in the medical uses of nucleic acids. For example, antisense, ribozymes, aptamer and RNA interference (RNAi) technologies are all being developed for potential therapeutic applications. Lots of research is being done in each specified fields and in fact there are already few drugs in “antisense category” and this time something really interesting has been reported by a Post Doc., Dr. Kim Woodrow in the field of RNA interference category. The following lines briefly summerise, what actually RNAis..
The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes including animals and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short fragments of ~20 nucleotides. One of the two strands of each fragment, known as the guide strand, is then incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand base pairs with a complementary sequence of a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. This process is known to spread systemically throughout the organism despite initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA. The importance of the siRNA lies in the fact that “RNAi is selective on gene expression” and hence can be used in the similar fashion like the antisense drugs (already a few drugs by ISIS, Serono and others). I did work on a few oligonucleotides (phosparothiamidates), while working in Innovasynth Technologies Limited Khopoli and know how difficult is to get the precursors of the antisense drugs. In 2006, Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm C. elegans.
Gene interference therapy is moving rapidly from basic research to application. The PLGA packaging these researchers chose is already approved as safe and non-toxic by the FDA, speeding the path to clinical trials for infectious agents such as HPV and HIV.
Congrats Dr.Kim and co workers for this achievement. The significance of this research is the fact that “a safe and effective administration of potential antiviral drugs - small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules using densely-loaded nanoparticles made of a biodegradable polymer known as PLGA. The researchers created a stable "time release" vehicle for delivery of siRNAs to sensitive mucosal tissue like that of the female reproductive system.
Monday, December 8, 2008
Can Antisense drugs revolutionize the drug discovery ?
Monday, March 1, 2021
FDA Approves Amondys 45 (casimersen) Injection for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) in Patients Amenable to Skipping Exon 45
In continuation of my update on antisense oligonucleotides
Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. the leader in precision genetic medicine for rare diseases, today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Amondys 45 (casimersen). Amondys 45 is an antisense oligonucleotide from Sarepta’s phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) platform, indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients with a confirmed mutation amenable to exon 45 skipping. This indication is based on a statistically significant increase in dystrophin production in skeletal muscle observed in patients treated with Amondys 45, which is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit for those patients who are exon 45 amenable. Consistent with the accelerated approval pathway, the continued approval of Amondys 45 may be contingent on confirmation of a clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The ESSENCE trial – a placebo-controlled confirmatory trial to support the Amondys 45 approval – is ongoing and expected to conclude in 2024.
Although kidney toxicity was not observed in the clinical studies with Amondys 45, kidney toxicity, including potentially fatal glomerulonephritis, has been observed after administration of some antisense oligonucleotides. Kidney function should be monitored in patients taking Amondys 45. In the clinical trial, the most common adverse reactions observed in at least 20% of patients treated with Amondys 45 and at least 5% more frequently than in placebo were (Amondys 45, placebo): upper respiratory tract infections (65%, 55%), cough (33%, 26%), fever (33%, 23%), headache (32%, 19%), joint pain (21%, 10%), and pain in mouth and throat (21%, 7%).
“This is an important day for Sarepta and, far more importantly, for the patients that we serve. After years of scientific commitment, investment and development, the approval of Amondys 45, Sarepta’s third approved RNA therapy, offers treatment to the 8% of the DMD community who have a confirmed exon 45 amenable mutation,” said Doug Ingram, president and chief executive officer, Sarepta. “Along with our other approved RNA therapies, we can now offer treatment options for nearly 30% of Duchenne patients in the U.S. And our commitment to bring therapies to the greatest percentage of the DMD community as soon as possible continues.”
“Decades of research and commitment have fueled and now accelerate our progress towards new treatments for Duchenne,” said Marissa Penrod, founder of Team Joseph and parent of an 18-year old with Duchenne. “The extraordinary diligence and persistence of the Duchenne community – patients and families, clinicians and researchers – have led us to today’s approval, where we now have exon-skipping treatments for almost a third of those with Duchenne.”
Saturday, October 10, 2009
Telomerase & Telomerase inhibition.......
When I was working with my previous company (Innovasynth Technologies Limited, Khopoli), I had opportunity to learn lots of things (from Dr. Sergei Gryaznov of Geron Corporation) about the drugs with Telomerase inhibition activity. As for as my knowledge goes, there are many companies working on these class of compounds and hope in the days to come there will be many drugs from this class of compounds and antisense drugs.
About Telomerase :
Telomerase, is an enzyme that adds specific DNA sequence repeats to the 3' end of DNA strands in the telomerase regions, which are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. The telomeres contain condensed DNA material, giving stability to the chromosomes. The enzyme is a reverse transcriptase that carries its own RNA molecule. Though the existence of a compensatory shortening of telomere (telomerase) mechanism, was first predicted by Soviet biologist Alexey Olovnikov (1973), who also suggested the Telomere hypothesis of ageing and the Telomere relations to cancer. Carol Greider and Elizabeth Blackburn in 1985, discovered telomerase together with Jack Szostak. Greider and Blackburn have been awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Congrats for this remarkable achievement.
Telomerase inhibitors :
To safeguard against cancer, adult cells keep track of how many times that they have multiplied, and once they have reached a pre-set limit — often around 80 divisions — they die. Telomerase interferes with this record keeping. So if one can find a drug or gene therapy that interferes with telomerase, it could fight the unchecked growth of cancer cells. As per the claim by lead researcher (Mark Muller), 90% all cancer cells are telomerase rich. Geron corporation, is developing modified DNA molecule (for which Innovasynth, has tie up with Geron to provide the intermediate amidites). The oligonucleotides, which target the template region, or active site, of telomerase. Geron's work has focused oligonucleotides (GRN163 and GRN163L,) and as per the claim by the company, both of them have demonstrated highly potent telomerase inhibitory activity at very low concentrations in biochemical assays, various cellular systems and animal studies. Interestingly these compounds are direct enzyme inhibitors, not antisense compounds and smaller than typical antisense compounds or other oligonucleotide drug candidates. Both compounds use a special thiophosphoramidate chemical backbone and the company is hopeful of convincing clinical trial results. All the best...
Ref : 1. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2009/press.html
2. http://www.geron.com/products/productinformation/cancerdrug.aspx
Tuesday, March 24, 2020
FDA Approves Vyondys 53 (golodirsen) Injection for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) in Patients Amenable to Skipping Exon 53

“Today is monumental for Sarepta and, more importantly, for the DMD community,” said Doug Ingram, president and chief executive officer, Sarepta. “Vyondys 53, our second approved exon-skipping RNA therapy for DMD, may treat up to 8% of the DMD community, representing those patients who have a confirmed exon 53 amenable mutation. Along with EXONDYS 51® (eteplirsen), we now offer treatment options for approximately 20% of those with DMD in the U.S.”
“With the approval of Vyondys 53, up to another 8% of Duchenne families will have a therapy to treat this devastating disease,” said Pat Furlong, founding president and chief executive officer, Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy (PPMD). “For 25 years, PPMD has been working with researchers, clinicians, industry, and the Duchenne community to find treatments for all people living with Duchenne. And while we need to ensure that these approved therapies are accessible for patients, today we celebrate this approval and thank Sarepta for their continued leadership in the fight to end Duchenne.”
About Vyondys 53
Sunday, November 8, 2009
Antisense Therapeutics completes repeat-dosing toxicology studies for ATL1103
One can see the products under development...(by the same co)..
Saturday, October 3, 2009
NDA of Cladribine as a drug for Multiple Sclerosis !
 When I was working with Innovasynth Technologies, Khopoli, I worked in the field of "antisense drugs" and as the company has tie up with many MNCs (working with these class of compounds) I had many times interacted with Serono, Pharmaceuticals (US) for some of the intermediates (oligonucleotides). When I read this article, I am happy there are many drugs still to be established as antisense drugs and more over this NDA (new drug application) is something to cherish.
When I was working with Innovasynth Technologies, Khopoli, I worked in the field of "antisense drugs" and as the company has tie up with many MNCs (working with these class of compounds) I had many times interacted with Serono, Pharmaceuticals (US) for some of the intermediates (oligonucleotides). When I read this article, I am happy there are many drugs still to be established as antisense drugs and more over this NDA (new drug application) is something to cherish.We know that 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine, Cladribine (Leustatin) is drug used to treat hairy cell leukemia (leukemic reticuloendotheliosis).
As a purine analog, it is a synthetic anticancer agent that also suppresses the immune system. Chemically, it mimics the nucleoside adenosine and thus inhibits the enzyme adenosine deaminase, which interferes with the cell's ability to process DNA. It is easily destroyed by normal cells except for blood cells, with the result that it produces relatively few side effects and results in very little non-target cell loss.
Though it has been used to treat leukemic reticuloendotheliosis, other activities like B cell leukemias and lymphomas, such as mantle cell lymphoma are still to be established. Now EMD Serono has applied for this NDA with FDA. As per the claim by the company, Cladribine Tablets has the potential to be the first orally administered disease-modifying therapy available for people living with relapsing MS, as all disease-modifying therapies currently approved for the treatment of MS are parenteral therapies. Hope FDA will approve the drug and will help many patients with relapsing forms of multiple scleorosis will have a relief in the days to come..
Ref : http://www.emdserono.com/cmg.emdserono_us/en/images/Cladribine%20Tablets%20FDA%20Submission%20FINAL%20US%20FINAL_tcm115_44365.pdf
Sunday, December 21, 2008
A Deep Insight into the World Gene Therapy Market
Friday, May 20, 2011
Tuesday, August 7, 2012
OGX-427 Improves PFS in Prostate Cancer | News | Drug Discovery and Development Magazine
Sixty-four of 72 planned patients have been randomized to the study and data on 42 patients [22 who received OGX-427 plus prednisone and 20 who received prednisone alone] are now available at or beyond the 12 week assessment time point. Highlights are as follows:
Thursday, July 18, 2024
FDA Approves Wainua (eplontersen) for the Treatment of Adults with Polyneuropathy of Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis
"Many people living with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy are unable to fully enjoy their lives because of the relentless, progressive and debilitating effects of the disease," said Michael J. Polydefkis, M.D., professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and an investigator in the NEURO-TTRansform study. "Approval of Wainua represents a meaningful advancement in treatment, one that gives those who are living with transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy help managing the disease."
ATTRv-PN is a debilitating disease that leads to peripheral nerve damage with motor disability within five years of diagnosis and, without treatment, is generally fatal within a decade. Wainua is a ligand-conjugated antisense oligonucleotide (LICA) medicine designed to reduce the production of TTR protein at its source.
"The FDA approval of Wainua marks an important milestone for people living with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy, who will now have an effective, well-tolerated treatment that can be self-administered via auto-injector to combat this devastating disease," said Brett P. Monia, Ph.D., chief executive officer at Ionis. "It is also a pivotal moment for Ionis as Wainua will be the first in a steady cadence of potential commercial launches for the company. We are proud to have discovered and, together with AstraZeneca, developed Wainua, and are grateful to the patients, caregivers and investigators who participated in our clinical studies, as well as for the dedication of our scientists and researchers."
"People with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy, and other forms of amyloidosis, are often misdiagnosed since symptoms can mirror other conditions," said Isabelle Lousada, President and CEO, Amyloidosis Research Consortium "The path to getting an accurate diagnosis can often be a long, arduous journey and it is critical that a timely and accurate diagnosis is made not only for the individual experiencing symptoms but for their families and loved ones. It is exciting to see new innovations coming through and increased efforts to raise awareness in an area that has often been overlooked or neglected."
