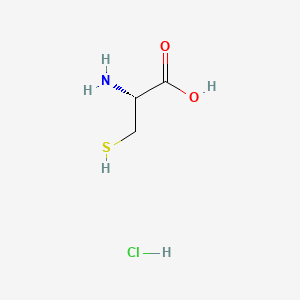
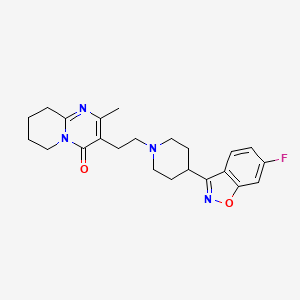
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NASDAQ:MDGL), a biopharmaceutical company focused on delivering novel therapeutics for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated approval for Rezdiffra (resmetirom) in conjunction with diet and exercise for the treatment of adults with noncirrhotic NASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis (consistent with stages F2 to F3 fibrosis). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in ongoing confirmatory trials.

Bill Sibold, Chief Executive Officer of Madrigal, stated, “NASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis is a serious and progressive liver disease that, until now, has not had an FDA-approved therapy. The accelerated approval of Rezdiffra is a culmination of more than 15 years of research from our founder Dr. Becky Taub and a small R&D team that took on one of the biggest challenges in drug development. This is a historic moment for the NASH field and represents the best of what our industry is capable of. We’re excited to deliver Rezdiffra to patients in need.”
Becky Taub, M.D., the Founder, Chief Medical Officer and President of Research & Development of Madrigal, stated, “Madrigal would like to thank the many patients who made the accelerated approval of Rezdiffra possible by participating in our clinical studies. We believe Rezdiffra will change the treatment paradigm for NASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis, giving physicians a liver-directed therapy to help improve fibrosis and resolve NASH before their patients progress to cirrhosis.”
Wayne Eskridge, Co-Founder and Chief Executive Officer of the Fatty Liver Foundation, stated, “This is a day of celebration for patients with NASH who have been waiting many years for the first approved therapy. I believe this approval milestone will bring new energy and momentum to the NASH community, accelerating our efforts to improve disease education, build care pathways, and expand investment in NASH research.”
Rezdiffra is a once-daily, oral THR-β agonist designed to target key underlying causes of NASH. The accelerated approval of Rezdiffra was based on results from the Phase 3 MAESTRO-NASH trial, which was recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine. MAESTRO-NASH is an ongoing pivotal, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 1,759 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH. Following 52 weeks of treatment, both 100 mg and 80 mg doses of Rezdiffra demonstrated statistically significant improvement compared to placebo on two primary endpoints: NASH resolution (including a reduction in the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD] activity score by ≥2 points) with no worsening of fibrosis, and an improvement in fibrosis by at least one stage with no worsening of the NAFLD activity score. Fibrosis improvement and NASH resolution were consistent regardless of age, gender, type 2 diabetes status, or fibrosis stage.
The Rezdiffra prescribing information does not include a liver biopsy requirement for diagnosis. The recommended dosage of Rezdiffra is based on actual body weight. For patients weighing <100 kg (220 lbs.), the recommended dosage is 80 mg orally once daily. For patients weighing ≥100 kg (220 lbs.), the recommended dosage is 100 mg orally once daily.
Stephen Harrison, M.D., Chairman for both Pinnacle Clinical Research and Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, Texas, Visiting Professor of Hepatology, Oxford University, and lead Principal Investigator of the MAESTRO studies, commented, “The approval of the first medication for NASH is a true game-changer for healthcare providers, the research community and, most importantly, patients living with this serious liver condition. Based on the robust efficacy and safety data generated in two large Phase 3 MAESTRO studies, I believe Rezdiffra will become the foundational therapy for patients with NASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis.”
Dr. Harrison continued, “Importantly, we continue to study Rezdiffra to determine if the positive results observed in the MAESTRO studies will lead to reduced risk of progression to cirrhosis, liver failure, need for liver transplant and premature mortality.”
MAESTRO-NASH remains ongoing as an outcomes study designed to generate confirmatory data that, if positive, will help verify clinical benefit and may support full approval. A second ongoing outcomes trial is evaluating progression to liver decompensation events in patients with well-compensated NASH cirrhosis treated with Rezdiffra versus placebo.
Rezdiffra should not be used in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. The most common adverse reactions reported in patients treated with Rezdiffra included diarrhea, nausea, pruritis, abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation, and dizziness. Diarrhea and nausea typically began early in treatment initiation and were mild to moderate in severity. A separate, noninvasive Phase 3 trial, MAESTRO-NAFLD-1, evaluated the safety and tolerability of Rezdiffra and contributed to the safety database supporting regulatory benefit-risk assessment.
Rezdiffra is expected to be available to patients in the U.S. in April and will be distributed through a limited specialty pharmacy network. Madrigal is committed to helping appropriate patients who may benefit from Rezdiffra access the medication through the Madrigal Patient Support program. This program is designed to help patients navigate insurance and affordability challenges and provide co-pay support for eligible patients. Madrigal has also established a patient assistance program (PAP) to help patients with no insurance access Rezdiffra.
Phase 3 MAESTRO-NASH Trial Results
MAESTRO-NASH is an ongoing Phase 3 trial that enrolled 1759 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH. Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive once-daily Rezdiffra at a dose of 80 mg or 100 mg or placebo. The two primary endpoints at week 52 were NASH resolution with no worsening of fibrosis and an improvement in fibrosis by at least one stage with no worsening of the NAFLD activity score. The key secondary endpoint was the percent change from baseline in LDL cholesterol at week 24.
Rezdiffra achieved both primary endpoints and the key secondary endpoint of the MAESTRO-NASH trial. Additionally, Rezdiffra improved liver enzymes, fibrosis biomarkers and imaging tests as compared with placebo. The primary results of the trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in February 2024.
Patients enrolled in the MAESTRO-NASH trial continue on therapy after the initial 52-week treatment period for up to 54 months to accrue and measure hepatic clinical outcome events including progression to cirrhosis on biopsy and hepatic decompensation events, as well as all-cause mortality. The 54-month outcomes portion of the trial is designed to generate confirmatory data that, if positive, will help verify Rezdiffra’s clinical benefit and may support full approval.
Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resmetirom