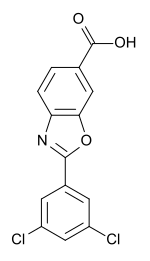
In continuation of my update on Tafamidis
Pfizer Inc. (NYSE: PFE) announced today that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accepted for filing the company’s New Drug Applications (NDAs) for tafamidis for the treatment of transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM). Pfizer has submitted two NDAs based on two forms of tafamidis: meglumine salt and free acid. Tafamidis is the only product to complete a Phase 3 trial evaluating its efficacy, safety, and tolerability in patients with ATTR-CM, a rare, fatal, and underdiagnosed condition.1,2
The tafamidis meglumine form (20 mg capsule) has been granted Priority Review. The FDA grants Priority Review to medicines that may offer significant advances in treatment or may provide a treatment where no adequate therapy exists. The target Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) action date for a decision by the FDA is in July 2019.
The tafamidis free acid form (61 mg capsule) will be under Standard Review. This form is bioequivalent to the 80 mg tafamidis meglumine dose, which was administered as four 20 mg capsules in the pivotal trial; it was developed for patient convenience to enable a single capsule for daily administration. The target PDUFA action date for a decision by the FDA is in November 2019.
“The diagnosis of ATTR-CM is often delayed, primarily because disease awareness is low and patients often present with symptoms similar to more common causes of heart failure. In fact, we believe less than one percent of patients living with this disease are currently diagnosed,” said Brenda Cooperstone MD, Senior Vice President and Chief Development Officer, Rare Disease, Pfizer Global Product Development. “The FDA’s filing acceptance is an encouraging step toward our goal of further raising awareness and providing a treatment option for ATTR-CM patients who are in desperate need of an approved pharmacologic therapy. We look forward to working with the FDA to bring the first treatment for this deadly disease to patients.”
The submission is based on findings from the pivotal Phase 3 Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy (ATTR-ACT) study, which evaluated the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of tafamidis meglumine compared to placebo for the treatment of patients with ATTR-CM. In the primary analysis of the study, tafamidis met the primary endpoint, demonstrating a significant reduction in the hierarchical combination of all-cause mortality and frequency of cardiovascular-related hospitalizations compared to placebo over a 30-month period in patients with wild-type or hereditary ATTR-CM (P=0.0006). Tafamidis was well tolerated, with an observed safety profile comparable to placebo.3 The primary results were presented in a Hot Line session at the ESC Congress 2018 in Munich, Germany, and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) in August 2018. Results from additional sub-group analyses were presented during the Late Breaking Clinical Trials session at the Heart Failure Society of America 22nd Annual Scientific Meeting in Nashville, TN, in September 2018. For more information on the ATTR-ACT trial, go to www.clinicaltrials.gov.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tafamidis





