

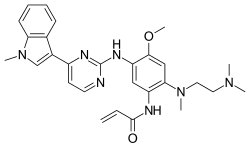
Osimertinib
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology a promising novel approach for a combined treatment of the most common type of lung cancer and associated secondary cancers in the central nervous system. The approach lies in combining two cancer drugs, with one compensating for a resistance side effect of the other.
In 20 to 40% of patients with cancer, metastasis (the development of secondary tumors) in the central nervous system (CNS) occurs. CNS metastasis impacts negatively on a patient's quality of life, and is associated with a poor health prognosis. In a form of cancer known as ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), CNS metastasis is known to persist when drugs targeting primary tumors are used. Now, Seiji Yano from Kanazawa University and colleagues have investigated the origins for the resistence to such drugs, and tested a new therapeutic strategy on a mouse model.
The researchers looked at the drug alectinib. Although used in standard treatments for advanced ALK-rearranged NSCLC, approximately 20 to 30% of patients treated with alectinib develop CNS metastasis, which is attributed to acquired resistance to the drug.
By treating mice first injected with tumor cells with alectinib daily for 16 weeks, the scientists obtained a mouse model displaying alectinib resistance. By biochemical analyses of the mouse brains, Yano and colleagues were able to link the resistance to the activation of a protein known as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). This activation is, in turn, a result of an increase in production of amphiregulin (AREG), a protein that binds to EGFR and in doing so 'activates' it.
Based on this insight, the researchers tested the effect of administering drugs used for inhibiting the action of EGFR in combination with alectinib treatment. The experiments showed that a combination treatment of alctinib with either erlotinib or osimertinib—two existing EGFR-inibiting drugs—prevented the progression of CNS metastasis, controlling the condition for over 30 days.
The scientists conclude that the combined use of alectinib and EGFR-inhibitors could overcome alectinib resistance in the mouse model of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LMC), a particular type of CNS metastasis. Quoting Yano and colleagues: "Our findings may provide rationale for clinical trials to investigate the effects of novel therapies dual-targeting ALK and EGFR in ALK-rearranged NSCLC with alectinib-resistant LMC."
Non-small-cell lung cancer
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) are the two types of lung cancer. 85% of all lung cancers are of the NSCLC type. NSCLCs are less sensitive to chemotherapy than SCLCs, making drug treatment of the highest importance.
Alectinib is a drug used for treating NSCLC, with good efficiency. However, 20-30% of patients taking the drug develop secondary cancer in the central nervous system (CNS), which is associated with an acquired resistance to alectinib. Seiji Yano from Kanazawa University and colleagues have now made progress towards a novel therapy against this resistance: a combination of alectinib with other drugs.
Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
The drugs that Yano and colleagues tested in combination with alectinib on a mouse model were of a type known as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors, including osimertinib and erlotinib. Both are being used as medication for treating NSCLC. The former was approved in 2017 as cancer treatment by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the European Commission. Yano and colleagues obtained results showing that EGFR inhibitors counteract resistance to alectinib and have therefore potential in novel therapies for NSCLC and secondary cancers in the CNS.
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2017-11-osimertinib-progression-free-survival-asian-egfr-mutated.html
