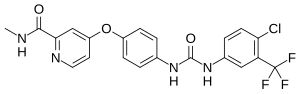
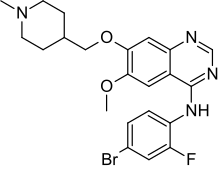
In continuation of my update on Sorafenib, Premetrexed, Vandetanib
"Though phase 1 studies are designed to evaluate the safety of a new therapy, we had strong preclinical evidence suggesting this novel drug combination could work against a variety of cancers, so we hoped that we would see a response in our patients in this early phase trial," said Andrew Poklepovic, M.D., lead investigator on the study. "With this trial, we established a safe dosing schedule, and we will now be testing the efficacy of the therapy in the phase 2 study."
The results of the clinical trial were recently published online by the journal Oncotarget (PMID: 27213589). The study enrolled 37 patients between October 2011 and December 2014. Of those patients, 36 received treatment and 33 were evaluated for response. One patient had a complete response, meaning all detectable traces of the tumor disappeared, while four patients had a partial response, which means that the tumor volume shrank by at least 30 percent. The therapy stabilized disease progression in an additional 15 patients, with some of these patients responding for up to a year. The therapy was found to be particularly active in breast cancer patients.
"Some dose-limiting toxicities associated with pemetrexed were observed in one cohort of patients, but those who were eligible were switched to the dosing schedule of the second cohort, which was found to safe and tolerable," says Poklepovic, medical oncologist and member of the Developmental Therapeutics research program at Massey as well as assistant professor in the Division of Hematology, Oncology and Palliative Care at the VCU School of Medicine.
The trial is based on pre-clinical research conducted by a team of Massey scientists led by Paul Dent, Ph.D., who is the Universal Corporation Chair in Cancer Cell Signaling and a member of the Cancer Cell Signaling research program at Massey, and Richard Moran, Ph.D., who recently retired after 22 years at Massey and more than four decades in the field. Pemetrexed was co-developed by Moran, and is now a first-line therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and mesothelioma. Sorafenib is used to treat liver, kidney and thyroid cancer. In 2011, a research team led by Dent and including Moran discovered that the two drugs synergize to induce profound killing of cancer cells through a toxic form of autophagy, a process that normally re-cycles components of cells to provide energy for maintaining cell growth and survival. The drug combination hyper-activated the autophagy process within cancer cells, causing them to literally eat themselves to death (PMID: 21622715).
The phase 2 study is not the only continuation of the research. Because the initial results of the phase 1 study were so promising, Dent started a new project to discover the best "third drug" that could act to further enhance the anti-cancer properties of the pemetrexed and sorafenib combination. This work has also recently been published in Oncotarget, and it showed that the combination therapy could be enhanced by a class of drugs known as ERBB1/2/4 inhibitors (PMID: 27015562).
"We discovered in mouse models of breast cancer that the drugs lapatinib and vandetanib significantly enhanced the anti-tumor effect of the pemetrexed and sorafenib therapy without any apparent toxicity to normal tissue. We made a nearly identical observation when adding the drug afatinib in experiments involving non-small cell lung cancer," says Dent. "Based on this data, we will be submitting a grant application to the National Cancer Institute for funding that will hopefully provide data that could allow us to open a future phase 1 trial testing the addition of an ERBB1/2/4 inhibitor to pemetrexed and sorafenib in patients with advanced solid tumors."
Dent was able to determine that ERBB1/2/4 inhibitors could increase the effectiveness of the combination therapy by using a novel technology called a multiplex assay. The multiplex assay is a broad, unbiased screening approach that allows researchers to simultaneously examine the levels of multiple hormones in the blood and determine the activities of enzymes in cancer cells. Using this technology, the researchers discovered that the enzyme ERBB1 was activated in response to the pemetrexed and sorafenib therapy.
"Unlike alternative methods where a certain degree of guesswork is required, the multiplex assay allowed us to observe exactly how the cancer cells responded to therapy," says Dent. "We were surprised to see that the enzyme ERBB1 was activated because it is ordinarily thought to protect cancer cells from chemotherapy. We went on to successfully use ERBB1/2/4 inhibitors as our third drug because of this unexpected data."
The multiplex assay provided Dent's team with such invaluable additional information about how the sorafenib and pemetrexed combination worked in the mouse models that they will now be using the assay in several of their clinical trials moving forward, including the new phase 2 trial of pemetrexed and sorafenib.
"The multiplex assay will allow us to track specific levels of hormones in the blood as patients undergo treatment, which could potentially give us a molecular 'fingerprint' of the point at which tumors develop resistance to the therapy," says Dent. "Ongoing preclinical experiments show that it could be possible to pinpoint exactly how the cancer cells are developing resistance to therapies, which might eventually allow oncologists to develop in real time a personalized therapy designed to overcome drug resistance in an individual patient's tumor."
Ref : http://www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/index.php?journal=oncotarget&page=article&op=view&path%5b%5d=9434