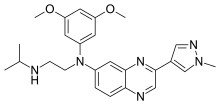
In continuation of my update on axitinib
Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany, which operates its biopharmaceutical business as EMD Serono in the US and Canada, and Pfizer Inc. (NYSE: PFE) today announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Bavencio (avelumab) in combination with Inlyta (axitinib) for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). This is the first FDA approval for an anti-PD-L1 therapy as part of a combination regimen for patients with advanced RCC. The approval of Bavencio in combination with Inlyta was based on positive results from the Phase III JAVELIN Renal 101 study (NCT02684006), in which the combination significantly improved median progression-free survival (PFS) compared with sunitinib by more than five months in the intent-to-treat (ITT) patient population (HR: 0.69 [95% CI: 0.56–0.84]; 2-sided p-value=0.0002; median PFS for Bavencio in combination with Inlyta: 13.8 months [95% CI: 11.1-NE]; sunitinib: 8.4 months [95% CI: 6.9-11.1]). The ITT population included patients regardless of PD-L1 expression and across IMDC (International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database) prognostic risk groups (favorable 21%, intermediate 62% and poor 16%).
“As we look to continue to improve outcomes for people with advanced RCC, new treatment approaches have the potential to benefit patients,” said Robert J. Motzer, M.D., Jack and Dorothy Byrne Chair in Clinical Oncology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, US, and principal investigator for JAVELIN Renal 101. “With today’s FDA approval of avelumab in combination with axitinib, we can now offer patients with advanced RCC a first-line treatment option that combines a PD-L1 immunotherapy with a well-known VEGFR TKI to provide a significant reduction in the risk of disease progression or death and doubling of the response rate compared with sunitinib.”
RCC is a type of cancer where PD-L1 expression may contribute to inhibition of the immune response against the tumor.2 It is also a highly vascular tumor, in which vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a key role.3
“A kidney cancer diagnosis is life-changing for both patients and their loved ones, and having a treatment strategy for their disease quickly becomes a priority,” said Dena Battle, President, KCCure. “The approval of new treatments such as Bavencio in combination with Inlyta gives patients with advanced RCC much-needed options.”
There is a significant unmet need for first-line treatments that delay progression and have an acceptable safety profile. Approximately 20% to 30% of patients are first diagnosed with RCC at the advanced stage, and 30% of patients treated for an earlier stage go on to develop metastases.4,5 About half of patients living with advanced RCC do not go on to receive additional treatment after first-line therapy,6,7 for reasons that may include poor performance status or adverse events from their initial treatment.6,8,9
“Today’s approval of Bavencio in combination with Inlyta builds on Pfizer’s long heritage in bringing innovation to the RCC community with the hopes of making a significant and meaningful impact on the lives of patients,” said Andy Schmeltz, Global President, Pfizer Oncology. “For more than 12 years, Pfizer has led the field in its commitment to developing new treatments for patients with advanced kidney cancer.”
“With today’s FDA approval of Bavencio in combination with Inlyta, we feel privileged that we can offer patients with first-line advanced renal cell carcinoma a new treatment option,” said Rehan Verjee, President, EMD Serono, and Global Head of Innovative Medicine Franchises, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany.
In JAVELIN Renal 101, the objective response rate (ORR) was doubled in the ITT population with Bavencio in combination with Inlyta versus sunitinib (51.4% [95% CI: 46.6-56.1] vs. 25.7% [95% CI: 21.7-30.0]). With a median overall survival (OS) follow-up of 19 months, data for the trial’s other primary endpoint of OS were immature, with 27% of deaths in the ITT population, and the trial is continuing as planned. The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were diarrhea, fatigue, hypertension, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, mucositis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, dysphonia, decreased appetite, hypothyroidism, rash, hepatotoxicity, cough, dyspnea, abdominal pain and headache. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 35% of patients receiving Bavencio in combination with Inlyta. The incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was higher with Bavencio in combination with Inlyta versus sunitinib.1 Findings from the study have been published in The New England Journal of Medicine.10
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) validated the Type II variation application for Bavencio in combination with Inlyta in advanced RCC in March 2019, and a supplemental application for Bavencio in combination with Inlyta in unresectable or metastatic RCC was submitted in Japan in January 2019.
The alliance is committed to providing patient access and reimbursement support through its CoverOne® program to patients who have been prescribed Bavencio. This program provides a spectrum of patient access and reimbursement support services intended to help US patients prescribed Bavencio receive appropriate access. CoverOne may be reached by phone at 844-8COVER1 (844-826-8371) or online at www.CoverOne.com.
Pfizer is committed to ensuring that patients who are prescribed Inlyta have access to this innovative therapy. Patients in the US have access to Pfizer Oncology Together™, which offers personalized support and financial assistance resources to help patients access their prescribed Pfizer Oncology medications. For more information, please call 1-877-744-5675 or visit PfizerOncologyTogether.com.
In an effort to streamline the patient enrollment process, EMD Serono and Pfizer have partnered to create a single enrollment form for the Bavencio and Inlyta combination for patients with advanced RCC that can be processed through both CoverOne and Pfizer Oncology Together. Each program will independently conduct the access and reimbursement activities for the product for which it is responsible.
Ref : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Axitinib
FDA Approves Bavencio (avelumab) Plus Inlyta (axitinib) Combination for Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma

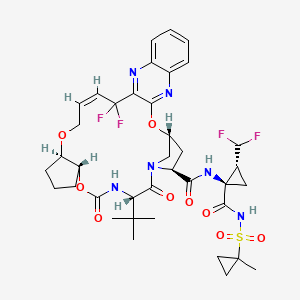
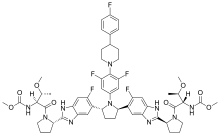 Pibrentasvir
Pibrentasvir
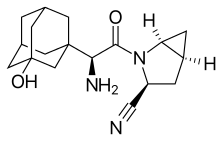 Saxagliptin and
Saxagliptin and