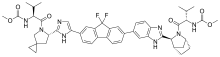
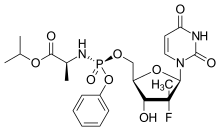
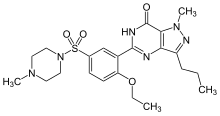
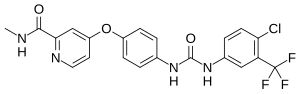
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (TSE: 4502) today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved NINLARO® (ixazomib) capsules, the first and only oral proteasome inhibitor, indicated in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least one prior therapy. NINLARO is a once-weekly pill.
Takeda submitted a New Drug Application for NINLARO to the FDA in July 2015, and in September NINLARO was granted Priority Review status with a PDUFA date of March 10, 2016, reflecting the profound and continuing unmet need for new treatments for multiple myeloma, a devastating, relapsing and incurable rare cancer.
“With the approval of NINLARO, we can now offer patients a once-weekly oral proteasome inhibitor as part of a highly active triplet therapy,” said Paul Richardson, M.D., Clinical Program Leader and Director of Clinical Research, Jerome Lipper Multiple Myeloma Center Institute Physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and investigator for TOURMALINE-MM1, the pivotal Phase 3 trial on which today’s approval is based. “We, as investigators of the TOURMALINE-MM1 trial, felt it was vital to conduct a comprehensive ‘real world’ evaluation of this combination that included some of the most common patient types in the relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma setting, such as older patients, patients with moderate renal impairment, light chain disease, and high risk cytogenetics. Further, we treated patients until disease progression to determine the sustainability of NINLARO in treating their relapsed/refractory disease. The TOURMALINE-MM1 data demonstrate convincingly that oral NINLARO-based triplet treatment is effective at extending progression-free survival, over and above the clinical benefit seen with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, with a tolerable safety profile.”