A model of how sarin and HI-6 are positioned in the protein acetylcholinesterase just before HI-6 removes sarin and restores the function of the protein. The model was developed by a combination of X-ray crystallography and quantum chemical calculations. Sarin in magenta, HI6 in green, oxygen in red, phosphorus in orange and nitrogen in blue.

The nerve agent sarin causes a deadly overstimulation of the nervous system that can be stopped if treated with an antidote within minutes of poisoning. Today, a ground-breaking study has been published in PNAS, which in detail describes how such a drug works. Researchers at the Swedish Defence Research Agency, Umeå University and in Germany are behind the study.
Sarin is a colourless, odourless liquid fatal even at very low concentrations. Serious sarin poisoning causes visual disturbance, vomiting, breathing difficulties and, finally, death.
"Nerve agents are dreadful weapons, and our hope is for these results to lead to improved drugs against them," says Anders Allgardsson, Biochemist at the Swedish Defence Research Agency (FOI).
Nerve agents destroy the function of a very important protein in the nervous system called acetylcholinesterase. As long as the nerve agent is bound to the protein, the breakdown of an important signal substance is prevented. The antidote HI-6 removes the nerve agent and restores the function of the nervous system. Drugs against nerve agent poisoning have been used for a long time, still it has been unclear how they actually work.
After years of hard work, chemists from FOI and Umeå University are now presenting a three-dimensional structure that depicts the HI-6 moments before the bond between the nerve agent and the protein is broken. The structure gives a high-resolution image that, in detail, describes the individual positions of atoms and provides an understanding of how the bond breaks.
The scientific breakthrough was enabled by combining three-dimensional structural depictions with advanced calculations and biochemical experiments.
"With the help of X-ray crystallography, we could see weak traces of the signal we were looking for. As the signal was weak, we decided to integrate the data with quantum chemical methods. After demanding calculations on the supercomputer at the High Performance Computing Center North (HPC2N) at Umeå University, we finally succeeded," says Anna Linusson, Professor at the Department of Chemistry at Umeå University.
The calculations supported the theory that the weak signal in the X-ray crystallography data actually came from HI-6 and sarin. Important knowledge also fell into place after experiments where the system was disturbed by mutating the protein or by introducing isotopes.
"After seven years of work using many different techniques, we have finally been able to bring this to a successful close and can show a uniform picture of how HI-6 approaches sarin. It opens up for new opportunities in finding antidotes to sarin and other nerve agents by structure-based molecular design," says Anders Allgardsson.
Ref : http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2016/04/28/1523362113


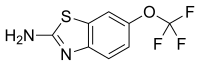 riluzole
riluzole
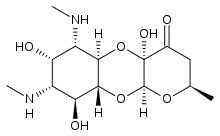
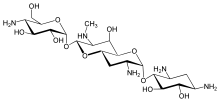 Apramycin
Apramycin Vernakalant
Vernakalant  Ibutilide
Ibutilide