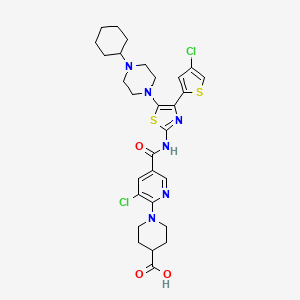
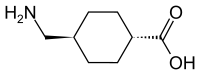
We know that, Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defense peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears as though antimicrobial peptides may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators.
Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides are generally between 12 and 50 amino acids. These peptides include two or more positively charged residues provided by arginine, lysine or, in acidic environments, histidine, and a large proportion (generally >50%) of hydrophobic residues. The secondary structures of these molecules follow 4 themes, including i) α-helical, ii) β-strandeddue to the presence of 2 or more disulfide bonds, iii) β-hairpin or loop due to the presence of a single disulfide bond and/or cyclization of the peptide chain, and iv) extended. Many of these peptides are unstructured in free solution, and fold into their final configuration upon partitioning into biological membranes. It contains hydrophilic amino acid residues aligned along one side and hydrophobic amino acid residues aligned along the opposite side of a helical molecule.. This amphipathicity of the antimicrobial peptides allows them to partition into the membrane lipid bilayer. The ability to associate with membranes is a definitive feature of antimicrobial peptides[ although membrane permeabilization is not necessary. These peptides have a variety of antimicrobial activities ranging from membrane permeabilization to action on a range of cytoplasmic targets.
--------------------------
Overuse of antibiotics has led to the spread of multi-resistant bacteria that do not respond to conventional treatments. Some 700 000 people worldwide die from antimicrobial resistance each year and the future social and economic costs will be huge if nothing is done. New treatment strategies for bacterial infections are desperately needed.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a promising alternative for treating infections because they kill bacteria by destroying their enclosing membrane, causing them to disintegrate.
AMPs are fast acting and non-specific; they attack many different bacterial strains. Infectious bacteria are less prone to developing resistance to AMPs, making them an exciting candidate for future treatment strategies.
However, few AMP-based therapies are available because they have low stability – they quickly degrade in storage and during treatment. The challenge is to get AMPs to the site of an infection in the dosage needed and without degradation.
The EU-funded FORMAMP project developed nanotechnology-based carriers to deliver AMPs directly to infected tissue. Encasing AMPs in nanoparticles helped protect them from degradation, with impressive implications.
“FORMAMP showed that structured nanoparticles are efficient delivery vehicles for a range of antimicrobial peptides needed for effective therapy,” explains project coordinator Lovisa Ringstad of RISE, Research Institutes of Sweden.
“Nanoparticles can overcome the major obstacle to peptide-based therapies that promise much in the fight against antimicrobial-resistant infections. For example, in the project we identified highly effective AMPs to combat tuberculosis. This is so promising that we are now seeking collaborators and funding for further development and to move towards eventual clinical testing.”
Fast, controlled delivery
Secondary skin infections in wounds and burns can involve several varieties of infectious bacteria – so a non-specific AMP offers obvious benefits. FORMAMP developed cream and gel formulations that are effective in delivering AMPs to the infected site and releasing them at a controlled rate.
To combat tuberculosis infections, researchers loaded porous silica nanoparticles with specially selected AMPs. Selected nanoparticles also proved very effective in penetrating the bacterial biofilm present in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients and in wound infections that can act as a significant barrier to otherwise effective treatments.
And the benefits go beyond the ‘magic bullet’ effect of the nanoparticles, says Ringstad. “Most conventional antibiotics are delivered through pills or injections, and if they underperform then more are prescribed. We have focused on treating skin and lung infection locally, thereby reducing exposure and making treatment easier for the patient. Local delivery strategies using nanoparticles can be more cost-effective, as they use less of the active ingredient, and have fewer side effects for the same reason.”
FORMAMP was a proof-of-concept, preclinical laboratory-based project. The researchers explored several nanoparticles, such as porous silica particles, liquid crystaline nanoparticles and dendrimers – star-shaped macromolecules. Desirable properties included non-toxicity and the ability to absorb, protect and release AMPs.
The project examined skin-wound and pulmonary infections, and specialist partners provided a range of AMPs known to work with these conditions.
“One important result concerned the effect of nanoparticles on biofilms,” explains Ringstad. “Biofilms are aggregations of infectious bacteria which protect the infected area against antibiotics and other therapies – they are common in many types of infection and are difficult to penetrate. We found that when nanoparticles are loaded with AMPs then the degradation of the biofilm was significantly improved. This ability to successfully attack biofilms is a very significant result for treating conditions such as cystic fibrosis and burn wound infections.”
The research resulted in many scientific publications and several promising patents that should benefit the SME partners.
Ringstad emphasizes the importance of FORMAMP results. “The nanoparticle delivery mechanism is not limited to treating infections – it could be used in a broad range of therapies. With further research, nanotherapeutics could possibly deliver more effective treatments with fewer side effects and at a lower cost for a wide range of conditions”.
---------------------------------
More at :