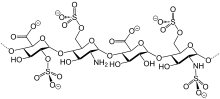
In continuation of my update on Teduglutide

Takeda Pharmaceuticals, U.S.A., Inc. (“Takeda”), announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved extending the indication of Gattex(teduglutide) for injection to pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS) who need additional nutrition or fluids from intravenous (IV) feeding (parenteral support).
In children, SBS is a life-threatening, chronic, and rare malabsorption disorder resulting from surgical removal of a large portion of the intestine, which is typically due to congenital or acquired conditions of the newborn or trauma.2-4 Children with SBS are unable to absorb enough nutrients and fluids from what they eat and drink alone.2 A goal of SBS treatment is to restore the remaining intestine’s ability to absorb nutrients and reduce long-term dependence on parenteral support (PS).
“As a pediatric gastroenterologist, one of my main treatment goals for children with SBS is to reduce their dependency on parenteral support,” said Beth Carter, MD, Medical Director of Intestinal Rehabilitation and Nutrition Support, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles. “I’m pleased that patients have access to a medication that may help them reach that goal.”
Gattex is the first and only medicine that mimics naturally occurring glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP-2), which helps the remaining intestine absorb more nutrients.1 In a pharmacodynamic study in adults, Gattex was shown to improve the amount of fluids absorbed by the intestines.
“Addressing high unmet needs of patients with complex and debilitating gastrointestinal (GI) conditions is a focus of Takeda’s work,” said Andrew Grimm, Global Clinical Development Lead, Takeda. “As the first U.S.-approved therapy in pediatric SBS patients dependent on PS that improves absorption, Gattex offers these patients new hope to reduce PS requirements and the potential for PS independence. This approval underscores Takeda’s commitment to patients with rare and devastating GI conditions like SBS.”
In a 24-week pediatric study, Gattex helped reduce the volume of daily PS required and time spent administering PS. Some children even achieved complete freedom from PS.1 Fifty- nine pediatric patients with SBS aged 1 year through 17 years chose whether to receive Gattex or standard of care (SOC). Patients who chose to receive Gattex treatment were subsequently randomized in a double-blind manner to 0.025 mg/kg/day (n=24) or 0.05 mg/kg/day (n=26), while 9 patients enrolled in the SOC arm. The recommended dosage of Gattex is 0.05 mg/kg/day. Randomization to the Gattex dose groups was stratified by age.
At the end of the 24-week study, 69% of patients (18/26) who took Gattex 0.05 mg/kg each day reduced PS volume by 20% or more. Based on patient-diary data, patients who received Gattex 0.05 mg/kg/day experienced a 42% mean reduction in PS volume (mL/kg/day) from baseline (-23 mL/kg/day from baseline). At week 24, 38% of patients (10/26) were able to reduce PS infusion by at least 1 day per week. Patients reduced their PS infusion time by 3 hours per day on average compared to baseline. In addition, during this study 3 out of 26 (12%) children who received Gattex 0.05 mg/kg/day completely weaned off PS.
Gattex has a demonstrated safety profile that is similar overall in pediatric and adult patients. The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) seen in adult patients treated with Gattex in clinical trials were abdominal pain, nausea, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal distension, injection site reaction, vomiting, fluid overload, and hypersensitivity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teduglutide