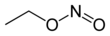



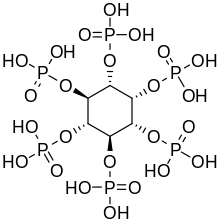
"Calcification occurs when calcium phosphate crystals are deposited in tissue," explains Jean-Christophe Leroux, professor of drug formulation and delivery at ETH Zurich. "The compound adheres to calcium phosphate crystals, inhibiting their growth."
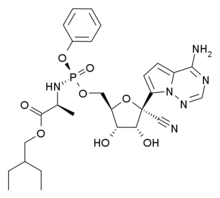


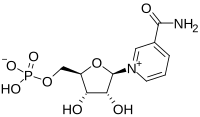
The drug cabotegravir is given every two months. It was 89 percent more effective at preventing HIV infection than Truvada pills, but both reduced the risk, the Associated Press reported. The study, which took place in Africa, was stopped early due to the promising results. The new findings echo those announced earlier this year from a study that compared the shots against the daily pills in gay men, the AP reported.
EMD Serono, the healthcare business sector of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany in the US and Canada, announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Tepmetko (tepotinib) following Priority Review for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping alterations. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The approval is based on results from the pivotal Phase II VISION study evaluating Tepmetko as monotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations.
"METex14 skipping occurs in approximately 3% to 4% of NSCLC cases, and patients with this aggressive lung cancer are often elderly and face a poor clinical prognosis," said Paul K. Paik, M.D., VISION primary investigator and Clinical Director, Thoracic Oncology Service, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. "There is a pressing need for targeted treatments that have the potential to generate durable anti-tumor activity and improve the lives of patients with this challenging disease. Tepmetko offers an important and welcome new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring these genetic mutations."
"In recent years, the treatment of lung cancer has seen powerful progress in the understanding of the genetic mutations that lead to tumor growth, resistance and progression," said Andrea Ferris, President and CEO of LUNGevity. "The availability of a new precision medicine for NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations advances patient access to targeted treatment and underscores the importance of routine comprehensive biomarker testing for patients with this challenging cancer."
Tepmetko is the first and only FDA approved MET inhibitor that offers once-daily oral dosing and is administered as two 225 mg tablets (450 mg). Patients with metastatic NSCLC should be selected for treatment with Tepmetko based on the presence of MET exon 14 skipping alterations.
"This approval of Tepmetko by the FDA is an important milestone on our mission to significantly improve the treatment of cancer where MET plays a driving role," said Danny Bar-Zohar, M.D., Global Head of Development for the Healthcare business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. "Our focus now is to ensure Tepmetko is accessible to patients in the United States and fully integrated into clinical practice given the important advance it represents for indicated patients as an oral once-a-day precision medicine."
EMD Serono, the healthcare business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany in the US and Canada, is committed to providing patient access and reimbursement support for eligible Tepmetko patients through its Oncology Navigation Center™ (ONC) program in the US. ONC provides a spectrum of patient access and reimbursement support services intended to help US patients receive appropriate treatment access. ONC may be reached at 1-844-662-3631 (844-ONC-EMD1) between 8am-8pm Eastern Time, Monday through Friday, or by visiting OncNavigationCenter.com.
Tepmetko was the first oral MET inhibitor to receive a regulatory approval anywhere in the world for the treatment of advanced NSCLC harboring MET gene alterations, with its approval in Japan in March 2020. The FDA completed its review of Tepmetko under its Real-Time Oncology Review pilot program after previously granting the medicine Breakthrough Therapy Designation. The FDA also recently granted Tepmetko Orphan Drug Designation (ODD).
A Marketing Authorization Application for tepotinib for a similar indication was validated by the European Medicines Agency in November 2020. Applications have also been submitted in Australia, Switzerland, and Canada under the FDA's Project Orbis initiative, which provides a framework for concurrent submission and review of oncology medicines among international partners.1
In the study, Tepmetko demonstrated an overall response rate of 43% (95% CI, 32–56) in treatment-naïve patients (n=69) and 43% (95% CI, 33-55) in previously treated patients (n=83). Median duration of response (DOR) was 10.8 months (95% CI, 6.9-NE) and 11.1 months (95% CI, 9.5-18.5) among treatment-naïve and previously treated patients, respectively. Duration of response of six months or more occurred among 67% of treatment-naïve patients and 75% of previously treated patients, and duration of response of nine months or more occurred among 30% of treatment-naïve patients and 50% of previously treated patients.3
The safety population included 255 patients with NSCLC positive for METex14 skipping alterations, who received Tepmetko in the VISION study. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in one patient (0.4%) due to pneumonitis, one patient (0.4%) due to hepatic failure, and one patient (0.4%) due to dyspnea from fluid overload. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received Tepmetko. Serious adverse reactions occurring in >2% of patients included pleural effusion (7%), pneumonia (5%), edema (3.9%), dyspnea (3.9%), general health deterioration (3.5%), pulmonary embolism (2%), and musculoskeletal pain (2%). The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients who received Tepmetko were edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea.
G1 Therapeutics, Inc. (Nasdaq: GTHX), a commercial-stage oncology company, announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Cosela (trilaciclib) for injection to decrease the incidence of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in adult patients when administered prior to a platinum/etoposide-containing regimen or topotecan-containing regimen for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). It is the first and only therapy designed to help protect bone marrow (myeloprotection) when administered prior to treatment with chemotherapy. Cosela is expected to be commercially available through G1’s specialty distributor partner network in early March.
“The approval of trilaciclib (Cosela) is an important advance in the treatment of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer receiving chemotherapy,” said Dr. Jeffrey Crawford, Geller Professor for Research in Cancer in the Department of Medicine and Duke Cancer Institute. “The most serious and life-threatening side effect of chemotherapy is myelosuppression, or damage to the bone marrow, resulting in reduced white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. Chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression may lead to increased risks of infection, severe anemia, and/or bleeding. These complications impact patients’ quality of life and may also result in chemotherapy dose reductions and delays. To date, approaches have included the use of growth factor agents to accelerate blood cell recovery after the bone marrow injury has occurred, along with antibiotics and transfusions as needed. By contrast, trilaciclib provides the first proactive approach to myelosuppression through a unique mechanism of action that helps protect the bone marrow from damage by chemotherapy. In clinical trials, the addition of trilaciclib to extensive-stage small cell lung cancer chemotherapy treatment regimens reduced myelosuppression and improved clinical outcomes. The good news is that these benefits of trilaciclib will now be available for our patients in clinical practice.”
Chemotherapy is an effective and important weapon against cancer. However, chemotherapy does not differentiate between healthy cells and cancer cells. It kills both, including important hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in the bone marrow that produce white blood cells (immune cells that help fight infection), red blood cells (cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues), and platelets (cells that prevent bleeding from cancer, surgeries, chronic diseases, and injuries). This chemotherapy-induced bone marrow damage, known as myelosuppression, can lead to increased risk of infection, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and other complications. Myeloprotection is a novel approach of protecting HSPCs in the bone marrow from chemotherapy-induced damage. This approach can help reduce some chemotherapy-related toxicity, making chemotherapy safer and more tolerable, while also reducing the need for reactive rescue interventions.
“Chemotherapy is the most effective and widely used approach to treating people diagnosed with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer; however, standard of care chemotherapy regimens are highly myelosuppressive and can lead to costly hospitalizations and rescue interventions,” said Jack Bailey, Chief Executive Officer at G1 Therapeutics. “Cosela will help change the chemotherapy experience for people who are battling ES-SCLC. G1 is proud to deliver Cosela to patients and their families as the first and only therapy to help protect against chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression.”
Cosela is administered intravenously as a 30-minute infusion within four hours prior to the start of chemotherapy and is the first FDA-approved therapy that helps provide proactive, multilineage protection from chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. The approval of Cosela is based on data from three randomized, placebo-controlled trials that showed patients receiving Cosela prior to the start of chemotherapy had clinically meaningful and statistically significant reduction in the duration and severity of neutropenia. Data also showed a positive impact on red blood cell transfusions and other myeloprotective measures. The trials evaluated Cosela in combination with carboplatin/etoposide (+/- the immunotherapy atezolizumab) and topotecan chemotherapy regimens. Approximately 90% of all patients with ES-SCLC will receive at least one of these regimens during the course of their treatment.
The majority of adverse reactions reported with Cosela were mild to moderate in severity. The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were fatigue, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pneumonia. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 30% of patients receiving Cosela. Serious adverse reactions reported in >3% of patients who received Cosela included respiratory failure, hemorrhage, and thrombosis. Grade 3/4 hematological adverse reactions occurring in patients treated with Cosela and placebo included neutropenia (32% and 69%), febrile neutropenia (3% and 9%), anemia (16% and 34%), thrombocytopenia (18% and 33%), and leukopenia (4% and 17%), respectively.
“Quite often, people diagnosed with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer rely on chemotherapy to not only extend their lives, but also to acutely alleviate their symptoms,” said Bonnie J. Addario, lung cancer survivor, co-founder and board chair of the Go2 Foundation for Lung Cancer. “Unfortunately, the vast majority will experience chemotherapy-induced side effects, resulting in dose delays and reductions, and increased utilization of healthcare services. G1 shares our organization’s goal to improve the quality of life of those diagnosed with lung cancer and to transform survivorship among people living with this insidious disease. We are thrilled to see new advancements that can help improve the lives of those living with small cell lung cancer.”
Approximately 30,000 small cell lung cancer patients are treated in the United States annually. G1 is committed to helping patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in the U.S. gain access to treatment with Cosela. For more information on access and affordability programs, patients and providers should call the G1toOne support center at 833-G1toONE (833-418-6663) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern time.
G1 received Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the FDA in 2019 based on positive data in small cell lung cancer patients from three randomized Phase 2 clinical trials. As is common with breakthrough-designated products that receive priority review, G1 will conduct certain post-marketing activities, including in vitro drug-drug interaction and metabolism studies, and a clinical trial to assess impact of trilaciclib on disease progression or survival in patients with ES-SCLC with chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression treated with a platinum/etoposide-containing or topotecan-containing regimen with at least a two year follow up. G1 intends to initiate the post-approval clinical trial in 2022.
Cosela (trilaciclib) Co-Promotion Agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim
In June 2020, G1 announced a three-year co-promotion agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim for Cosela in small cell lung cancer in the U.S. and Puerto Rico. G1 will lead marketing, market access and medical engagement initiatives for Cosela. The Boehringer Ingelheim oncology commercial team, well-established in lung cancer, will lead sales force engagement initiatives. G1 will book revenue and retain development and commercialization rights to Cosela and pay Boehringer Ingelheim a promotional fee based on net sales. The three-year agreement does not extend to additional indications that G1 is evaluating for trilaciclib. Press release details of the G1/ Boehringer Ingelheim agreement can be found here.