Sense oligonucleotide antidote reverses actions of antisense antithrombotic drug, prevents bleeding
Tuesday, November 24, 2015
Sense oligonucleotide antidote reverses actions of antisense antithrombotic drug, prevents bleeding
Sense oligonucleotide antidote reverses actions of antisense antithrombotic drug, prevents bleeding
Tuesday, March 24, 2020
FDA Approves Vyondys 53 (golodirsen) Injection for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) in Patients Amenable to Skipping Exon 53

“Today is monumental for Sarepta and, more importantly, for the DMD community,” said Doug Ingram, president and chief executive officer, Sarepta. “Vyondys 53, our second approved exon-skipping RNA therapy for DMD, may treat up to 8% of the DMD community, representing those patients who have a confirmed exon 53 amenable mutation. Along with EXONDYS 51® (eteplirsen), we now offer treatment options for approximately 20% of those with DMD in the U.S.”
“With the approval of Vyondys 53, up to another 8% of Duchenne families will have a therapy to treat this devastating disease,” said Pat Furlong, founding president and chief executive officer, Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy (PPMD). “For 25 years, PPMD has been working with researchers, clinicians, industry, and the Duchenne community to find treatments for all people living with Duchenne. And while we need to ensure that these approved therapies are accessible for patients, today we celebrate this approval and thank Sarepta for their continued leadership in the fight to end Duchenne.”
About Vyondys 53
Saturday, May 24, 2014
Compound reverses symptoms of Alzheimer's disease in mice
Farr cautioned that the experiment was conducted in a mouse model. Like any drug, before an antisense compound could be tested in human clinical trials, toxicity tests need to be completed.
Antisense is a strand of molecules that bind to messenger RNA, launching a cascade of cellular events that turns off a certain gene.
In this case, OL-1 blocks the translation of RNA, which triggers a process that keeps excess amyloid beta protein from being produced. The specific antisense significantly decreased the over expression of a substance called amyloid beta protein precursor, which normalized the amount of amyloid beta protein in the body. Excess amyloid beta protein is believed to be partially responsible for the formation of plaque in
the brain of patients who have Alzheimer's disease.
Scientists tested OL-1 in a type of mouse that overexpresses a mutant form of the human amyloid beta precursor gene. Previously they had tested the substance in a mouse model that has a natural mutation causing it to overproduce mouse amyloid beta. Like people who have Alzheimer's disease, both types of mice have age-related impairments in learning and memory, elevated levels of amyloid beta protein that stay in the brain and increased inflammation and oxidative damage to the hippocampus the part of the brain responsible for learning and memory.
"To be effective in humans, OL-1 would need to be effective at suppressing production of human amyloid beta protein," Farr said.
Scientists compared the mice that were genetically engineered to overproduce human amyloid beta protein with a wild strain, which served as the control. All of the wild strain received random antisense, while about half of the genetically engineered mice received random antisense and half received OL-1.
The mice were given a series of tests designed to measure memory, learning and appropriate behavior, such as going through a maze, exploring an unfamiliar location and recognizing an object.
Scientists found that learning and memory improved in the genetically engineered mice that received OL-1 compared to the genetically engineered mice that received random antisense. Learning and memory were the same among genetically engineered mice that received OL-1 and wild mice that received random antisense.
They also tested the effect of administering the drug through the central nervous system, so it crossed the blood brain barrier to enter the brain directly, and of giving it through a vein in the tail, so it circulated through the bloodstream in the body. They found where the drug was injected had little effect on learning and memory.
Ref http://iospress.metapress.com/content/px72758w0158103u/?issue=4&genre=article&spage=1005&issn=1387-2877&volume=40
Tuesday, September 11, 2018
New approach to kill specific bacteria could be alternative to antibiotics
"We were able to show that these drugs can zero in on and kill C. difficile bacteria while leaving other bacteria alone," said Arun Sharma, associate professor of pharmacology, Penn State College of Medicine. "We're still working to refine these drugs and make them even better, with the eventual goal of testing them clinically."
"These drugs are organism specific, meaning that they target only one kind of bacteria, kind of like smart antibiotics," Stewart said. "They're precise. And that's especially important with C. difficile infections because this bacteria is uniquely, selectively advantaged to exploit ecological disturbances in the human gut."
"Ideally, a treatment for C. difficile would have no effect on other bacteria," Stewart said.
"Our antisense antibiotics contain genetic material which is complementary to bacterial genetic material, so we designed our genetic material to target specific genes in C. difficile," Stewart said. "And when our genetic material binds to the bacterial genetic material, it prevents the expression of bacterial genes. And that can cause C. difficile to die."
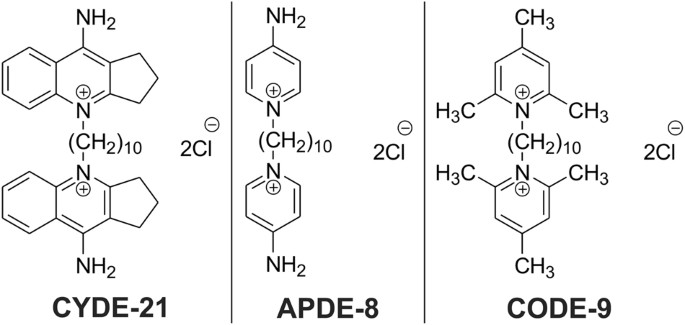
"Ultimately, we wanted these compounds to deliver the drug into the C. difficile bacteria without hurting other bacteria or the patient," Sharma said. "After testing these three, we found that one carrier in particular -- CYDE-21 -- was the best at delivering an effective dose of the drug into the bacteria."
Saturday, October 24, 2009
Phase III clinical study of trabedersen....
Ref :http://www.anticancer.de/index.php?id=38.
I found this video, interesting (mode of action of trabedersen)
Monday, March 1, 2021
FDA Approves Amondys 45 (casimersen) Injection for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) in Patients Amenable to Skipping Exon 45
In continuation of my update on antisense oligonucleotides
Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. the leader in precision genetic medicine for rare diseases, today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Amondys 45 (casimersen). Amondys 45 is an antisense oligonucleotide from Sarepta’s phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) platform, indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients with a confirmed mutation amenable to exon 45 skipping. This indication is based on a statistically significant increase in dystrophin production in skeletal muscle observed in patients treated with Amondys 45, which is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit for those patients who are exon 45 amenable. Consistent with the accelerated approval pathway, the continued approval of Amondys 45 may be contingent on confirmation of a clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The ESSENCE trial – a placebo-controlled confirmatory trial to support the Amondys 45 approval – is ongoing and expected to conclude in 2024.
Although kidney toxicity was not observed in the clinical studies with Amondys 45, kidney toxicity, including potentially fatal glomerulonephritis, has been observed after administration of some antisense oligonucleotides. Kidney function should be monitored in patients taking Amondys 45. In the clinical trial, the most common adverse reactions observed in at least 20% of patients treated with Amondys 45 and at least 5% more frequently than in placebo were (Amondys 45, placebo): upper respiratory tract infections (65%, 55%), cough (33%, 26%), fever (33%, 23%), headache (32%, 19%), joint pain (21%, 10%), and pain in mouth and throat (21%, 7%).
“This is an important day for Sarepta and, far more importantly, for the patients that we serve. After years of scientific commitment, investment and development, the approval of Amondys 45, Sarepta’s third approved RNA therapy, offers treatment to the 8% of the DMD community who have a confirmed exon 45 amenable mutation,” said Doug Ingram, president and chief executive officer, Sarepta. “Along with our other approved RNA therapies, we can now offer treatment options for nearly 30% of Duchenne patients in the U.S. And our commitment to bring therapies to the greatest percentage of the DMD community as soon as possible continues.”
“Decades of research and commitment have fueled and now accelerate our progress towards new treatments for Duchenne,” said Marissa Penrod, founder of Team Joseph and parent of an 18-year old with Duchenne. “The extraordinary diligence and persistence of the Duchenne community – patients and families, clinicians and researchers – have led us to today’s approval, where we now have exon-skipping treatments for almost a third of those with Duchenne.”
Thursday, July 18, 2024
FDA Approves Wainua (eplontersen) for the Treatment of Adults with Polyneuropathy of Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis
"Many people living with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy are unable to fully enjoy their lives because of the relentless, progressive and debilitating effects of the disease," said Michael J. Polydefkis, M.D., professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and an investigator in the NEURO-TTRansform study. "Approval of Wainua represents a meaningful advancement in treatment, one that gives those who are living with transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy help managing the disease."
ATTRv-PN is a debilitating disease that leads to peripheral nerve damage with motor disability within five years of diagnosis and, without treatment, is generally fatal within a decade. Wainua is a ligand-conjugated antisense oligonucleotide (LICA) medicine designed to reduce the production of TTR protein at its source.
"The FDA approval of Wainua marks an important milestone for people living with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy, who will now have an effective, well-tolerated treatment that can be self-administered via auto-injector to combat this devastating disease," said Brett P. Monia, Ph.D., chief executive officer at Ionis. "It is also a pivotal moment for Ionis as Wainua will be the first in a steady cadence of potential commercial launches for the company. We are proud to have discovered and, together with AstraZeneca, developed Wainua, and are grateful to the patients, caregivers and investigators who participated in our clinical studies, as well as for the dedication of our scientists and researchers."
"People with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloid polyneuropathy, and other forms of amyloidosis, are often misdiagnosed since symptoms can mirror other conditions," said Isabelle Lousada, President and CEO, Amyloidosis Research Consortium "The path to getting an accurate diagnosis can often be a long, arduous journey and it is critical that a timely and accurate diagnosis is made not only for the individual experiencing symptoms but for their families and loved ones. It is exciting to see new innovations coming through and increased efforts to raise awareness in an area that has often been overlooked or neglected."
Thursday, December 25, 2008
A new experimental drug "antagomir" (antisense oligonucleotide) as an anti- miR-21 agent..
Thum and colleagues discovered that miR-21 was expressed in the heart's fibroblast cells (cells that make the scaffolding of collagen or connective tissue that hold the shape of the organ) and were in greater numbers in lab mice bred to have heart failure and also in human tissue from patients who had heart failure.
In this study they showed that increasing expression of miR-21 changed the way that signals behaved in a previously unknown stress response pathway that involved the gene sprouty-1 and the MAP-kinase signaling pathway. In turn, increasing the activity of the MAP-kinase pathway led to a number of signs of heart failure, such as enhanced fibroblast survival, increased secretion of factors like fibroblast growth factor, tissue scarring (fibrosis), and cardiac dysfunction including cellular hypertrophy.
The researchers proved they could administer anti-miR-21 effectively to the heart by monitoring it with fluorescence staining. Then, in a mouse transaortic constriction model of human heart failure, they showed that anti-miR-21 silenced increased expression of miR-21 and corrected downstream changes in sprouty-1 and MAP-kinase signaling.
The interesting thing is their conclusion : Anti-miR-21, showed the most statistically significant improvement in the heart failure mouse model when given before induction of heart failure and for as long as three weeks afterward and it might be possible to target entire disease pathways with one drug. Contrats Dr. Thomas Thum.
Friday, November 20, 2009
Positive results from mipomersen- a new hope for FH sufferers...
Familial hypercholesterolemia (also spelled familial hypercholesterolaemia) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high low-density lipoprotein (LDL, "bad cholesterol") levels, in the blood and early cardiovascular disease. Many patients have mutations in the LDLR gene that encodes the LDL receptor protein, which normally removes LDL from the circulation, or apolipoprotein B (ApoB), which is the part of LDL that binds with the receptor; mutations in other genes are rare. Patients who have one abnormal copy (are heterozygous) of the LDLR gene may have premature cardiovascular disease at the age of 30 to 40. Having two abnormal copies (being homozygous) may cause severe cardiovascular disease in childhood. Heterozygous FH is a common genetic disorder, occurring in 1:500 people in most countries; homozygous FH is much rarer, occurring in 1 in a million births.
Heterozygous (FH) is normally treated with statins, bile acid sequestrants or other hypolipidemic agents that lower cholesterol levels. New cases are generally offered genetic counseling. Homozygous FH often does not respond to medical therapy and may require other treatments, including LDL apheresis (removal of LDL in a method similar to dialysis) and occasionally liver transplantation.
Recently, Genzyme Corp. and Isis Pharmaceuticals Inc have come up with some intresting results from the drug mipomersen [mipomersen - is an antisense oligonucleotide, with phosphorothioate linkage at 5'- postion and 2'-O-methoxymethyl moety] ( phase 3). As per the claim by the companies, the study met its primary endpoint in an intent-to-treat analysis, with a 25 percent reduction in LDL-cholesterol after 26 weeks of treatment, vs. 3 percent for placebo (p<0.001)>.
The trial met all of its secondary and tertiary endpoints, suggesting that mipomersen may offer potential benefits to patients beyond LDL-C reduction. Patients treated with mipomersen experienced a 27 percent reduction in apolipoprotein B vs. 3 percent for placebo; a 21 percent reduction in total cholesterol vs. 2 percent for placebo; and a 25 percent reduction in non-HDL cholesterol vs. 3 percent for placebo (all p<0.001).>Mipomersen patients’ HDL-C levels increased 15 percent (p=0.035 vs. placebo), which combined with the LDL-C reductions observed, resulted in improved LDL/HDL ratios, a ratio considered an important measure of cardiovascular risk. Mipomersen patients’ LDL/HDL ratios decreased by 34% (p<0.001>Mipomersen a representative of Isis’ leadership in the field of RNA targeted therapeutics will bring a sigh of relief to the sufferers of FH, in the days to come.
I had an opportunity to work with ISIS (as contract R & D, Innovasynth Technologies Limited, Khopoli) and really excited to see the results..
Ref : http://ir.isispharm.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=222170&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1356364&highlight=
Saturday, October 10, 2009
Telomerase & Telomerase inhibition.......
When I was working with my previous company (Innovasynth Technologies Limited, Khopoli), I had opportunity to learn lots of things (from Dr. Sergei Gryaznov of Geron Corporation) about the drugs with Telomerase inhibition activity. As for as my knowledge goes, there are many companies working on these class of compounds and hope in the days to come there will be many drugs from this class of compounds and antisense drugs.
About Telomerase :
Telomerase, is an enzyme that adds specific DNA sequence repeats to the 3' end of DNA strands in the telomerase regions, which are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. The telomeres contain condensed DNA material, giving stability to the chromosomes. The enzyme is a reverse transcriptase that carries its own RNA molecule. Though the existence of a compensatory shortening of telomere (telomerase) mechanism, was first predicted by Soviet biologist Alexey Olovnikov (1973), who also suggested the Telomere hypothesis of ageing and the Telomere relations to cancer. Carol Greider and Elizabeth Blackburn in 1985, discovered telomerase together with Jack Szostak. Greider and Blackburn have been awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Congrats for this remarkable achievement.
Telomerase inhibitors :
To safeguard against cancer, adult cells keep track of how many times that they have multiplied, and once they have reached a pre-set limit — often around 80 divisions — they die. Telomerase interferes with this record keeping. So if one can find a drug or gene therapy that interferes with telomerase, it could fight the unchecked growth of cancer cells. As per the claim by lead researcher (Mark Muller), 90% all cancer cells are telomerase rich. Geron corporation, is developing modified DNA molecule (for which Innovasynth, has tie up with Geron to provide the intermediate amidites). The oligonucleotides, which target the template region, or active site, of telomerase. Geron's work has focused oligonucleotides (GRN163 and GRN163L,) and as per the claim by the company, both of them have demonstrated highly potent telomerase inhibitory activity at very low concentrations in biochemical assays, various cellular systems and animal studies. Interestingly these compounds are direct enzyme inhibitors, not antisense compounds and smaller than typical antisense compounds or other oligonucleotide drug candidates. Both compounds use a special thiophosphoramidate chemical backbone and the company is hopeful of convincing clinical trial results. All the best...
Ref : 1. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2009/press.html
2. http://www.geron.com/products/productinformation/cancerdrug.aspx
Thursday, September 21, 2017
New drug shows promising results for treating spinal muscular atrophy
Tuesday, January 26, 2010
SPC3649 ( LNA- locked nucleic acid) - a new hope for hepatitis C.....
Monday, April 25, 2011
Tuesday, November 16, 2010
Regulus present advancements in microRNA platform at Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Society meeting
Regulus present advancements in microRNA platform at Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Society meeting

