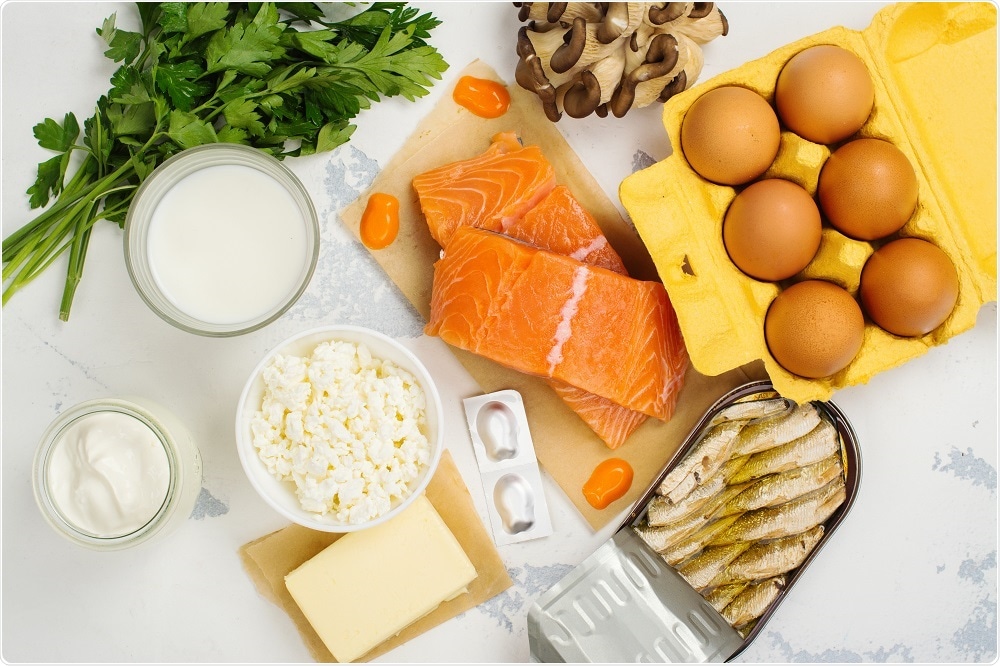
The study reinforces the existing theory that vitamin D helps defend against certain cancers. Exposure to sunlight stimulates the production of vitamin D by our skin. Vitamin D contributes to calcium level maintenance in our bodies, which in turn helps teeth, muscles and bones remain healthy. Aside from established benefits of vitamin D on bone diseases, evidence continues to emerge that vitamin D could be effective for other cancers and chronic diseases.
Yet more comprehensive research needs to be conducted, as to date, the majority of studies have been conducted throughout American and European populations, and more studies focusing on Asian populations are necessary.
It is vital to determine whether the effects are the same in non-Caucasian populations, since Vitamin D metabolism and concentrations differ dependant on ethnicity.
The study published by the BMJ was carried out to determine if vitamin D was linked to site specific and total cancer.
Data spanning nine public health centres across Japan was analysed, from 33,736 female and male participants between the ages of 40 and 69 years old.
Participants were required to disclose a comprehensive overview of their lifestyle, diet and medical history and have blood samples taken to assess their vitamin D levels. Factors such as seasons affected vitamin D levels; summer and autumn typically produced higher levels compared to spring or winter. Samples were then assigned to one of four groups, based on levels.
Researchers then monitored the study participants for a mean period of 16 years, during which 3,301 new cancer cases were registered.
Once multiple known cancer risk factors had been accounted for, including weight (BMI), physical activity, age, dietary factors, smoking and alcohol intake, researchers discovered that high levels of vitamin D reduced the overall risk of cancer by 20% in both women and men.
Higher levels were linked to a 30-50% lower relative risk of liver cancer, and more so in men than women. No cancers exhibited a higher risk connected to high vitamin D levels, and there was no evidence of a link to prostate or lung cancer.
Adjustments were made for dietary and other factors to confirm the strength of the findings, but this did little to affect the results. One limitation of the study was an insufficient number of organ specific cancers. In addition, even with the risk factor adjustments, there is no absolute certainty that the results were skewed by unidentified factors. For this reason, no concrete conclusions about cause and effect can be asserted.
The large sample size for overall cancer, large number of blood samples tested and the extensive follow up period were vital strengths of the study. The result reinforce the theory that vitamin D has a role in defending against the risk of cancer, but the authors emphasize that vitamin D may carry additional health benefits too, that were not measured in this study.
Further studies are needed to clarify the optimal concentrations (of vitamin D) for cancer prevention."
Further studies are needed to clarify the optimal concentrations (of vitamin D) for cancer prevention."Ref : https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2018-03/b-hvd030618.php